Action C7. Promoting population dispersion
Aims
The only non-toxic part of the yew is red and fleshy fruit. The plant produces it to disperse their seeds by frugivorous birds as thrushes. The main objective is to increase the natural spread of seeds by attracting frugivorous birds. The complementary objective is to promote the floristic diversity of habitat.
Actions
- Increasing the concentration density of “baiting plants” that produce fleshy fruits.
- Selective cutting and selection of shoots to foment fruit production of bait plants eliminate competition.
- Planting baiting species base near yew mother trees.
- Making selective cuts around yew producing base.
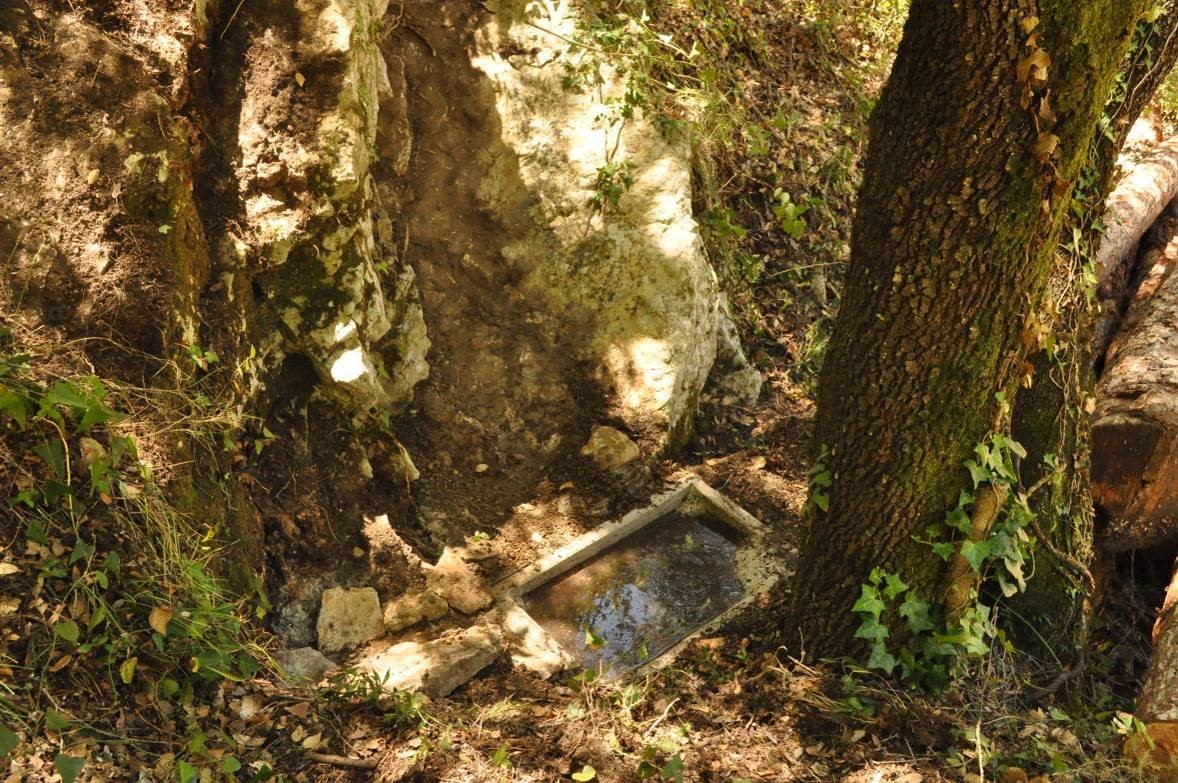
- Construction of troughs waterholes and ponds to attract birds.
Results
3702 seedlings of different “bait species” (fleshy fruit producers) were cultivated to attract birds to the yews. Selective cuts in 201 ha were also made and about on 1145 female yew. 900 feet of woody species were also treated.
12 birds drinkers scattered around the Llaberia forest were installed. Bait species also contribute to the diversification of habitat: in each yew forest seedlings from the own area are planted, from seed collected in the same place.
The female yew trees have begun to bear fruit after actuation and waterers are used by the scatterers.
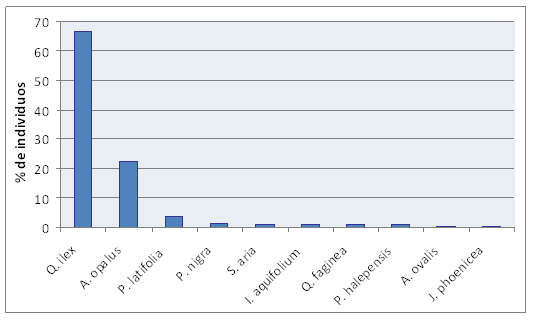
- Exemple d’espècies llenyoses que acompanyen el teix en un bosc mediterrani. Serra de Llaberia.
Areas
Tejeda de Cosp (Cardo), Sierra de Llaberia and Alta Garrotxa.
Calendar
1st quarter 2013 – 1st 2015
Results of camera trap surveys (2 cameras per trapping zone for a month) and points counts for birds during the aril fruiting (September-October of 2012 and 2013)
Herbivores (consumes leaves and bark of the yew)
- Domestic goat
- Roe deer
- Cow
- Wood mouse
- Eurasian red squirrel
- Hawfinch
- Beech marten
- Genet
- Common wood pigeon
- Jay
- Ring ouzel
- Song thrush (main disperser)
- Badger
- Fox
- Chaffinch
- Robin
- Blackbird
- Mistle thrush
- Humans (hunters, mushroom pickers, shepherds, naturalists, hikers.
- WildBoar
- Wildcat
- Seed predation is important
- Resident dispersers unimportant
- Key dispensers are migrant birds: Sing thrush and Ring ouzel
- Applied conclusion: mother yews must be made more visible for migrants and fruiting to be promoted.


